In recent times, the correlation between gut health and mental well-being has garnered significant attention in both scientific research and public discourse. While the significance of maintaining a healthy gut for physical well-being has been acknowledged for quite some time, emerging studies are illuminating the profound influence it exerts on our mental health and overall sense of well-being. This article seeks to delve into the complex interplay between gut health and mental well-being, revealing the intriguing connection between our gastrointestinal system and brain function.
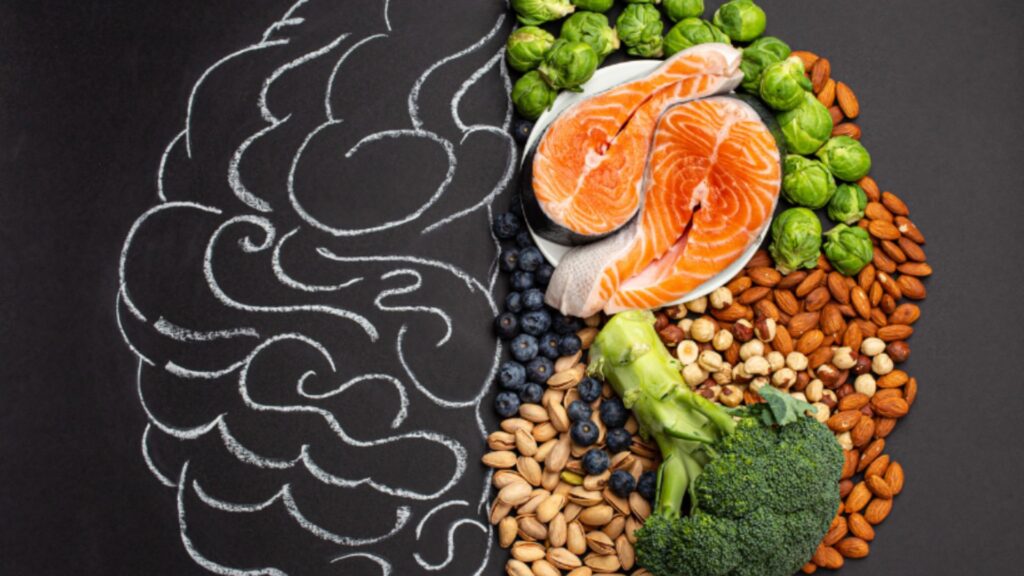

The Gut Microbiome
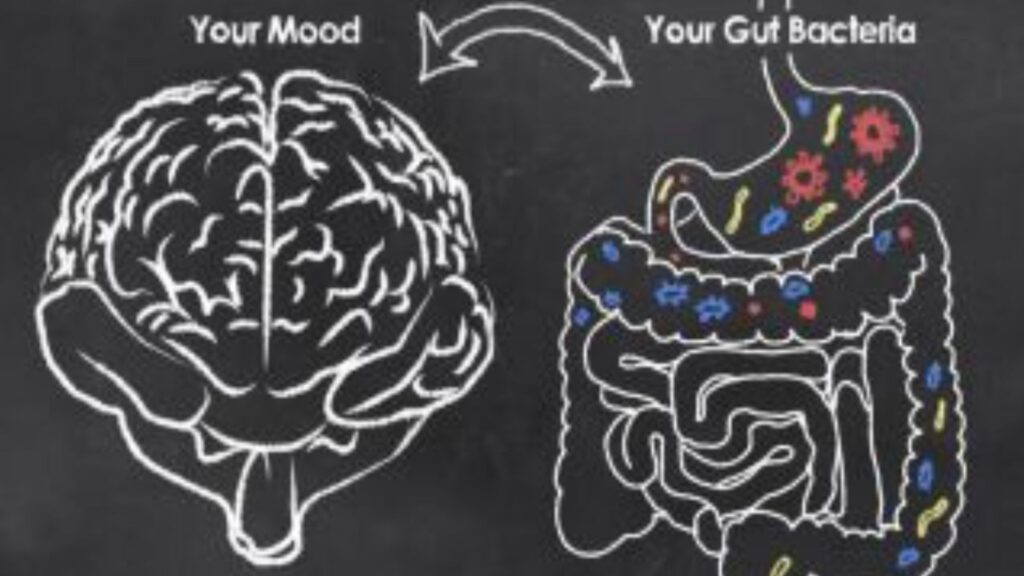
The gut-brain connection centres around the gut microbiome, an expansive network of microorganisms residing in our digestive system. This intricate community, composed of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microbes, serves pivotal functions in digestion, absorbing nutrients, and bolstering our immune system. Yet, its impact transcends mere digestive processes, intricately intertwining with the pathways of our brain.
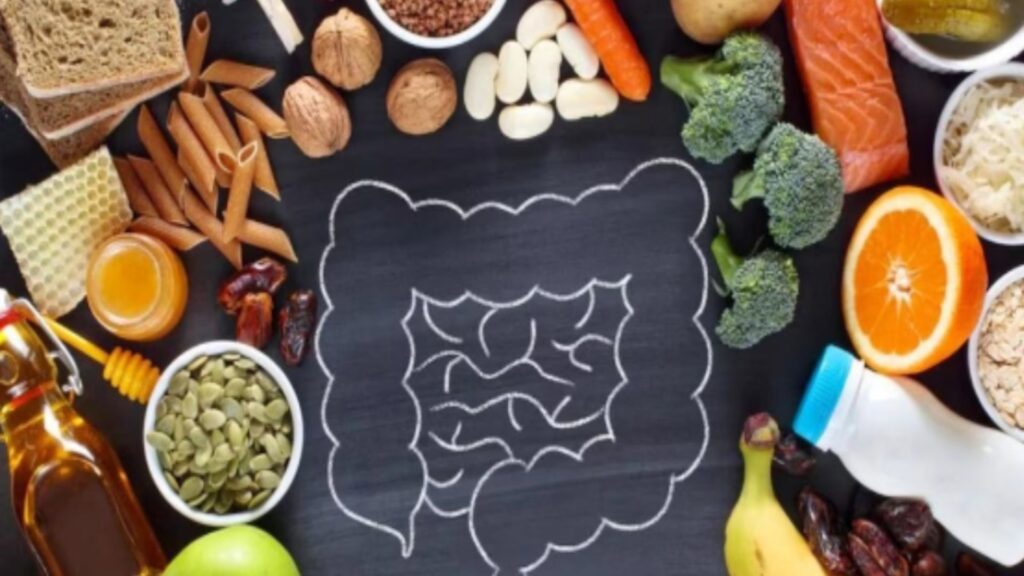

Impact on Mental Health
Studies indicate that the makeup and richness of the gut microbiome play a pivotal role in shaping our mental well-being and cognitive abilities. Disturbances in the balance of gut bacteria, termed dysbiosis, have been associated with a range of mental health disorders such as anxiety, depression, and even serious conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. This highlights the intricate relationship between the gut microbiota and mental health, underscoring the importance of maintaining a healthy balance in our gastrointestinal system for optimal brain function and emotional stability.
Communication Pathways
But how does the gut communicate with the brain? The gut-brain axis serves as a two-way communication network between the gut and the brain. Through neurotransmitters, hormones, and immune molecules, signals travel along this axis, influencing mood, behaviour, and cognitive processes. This highlights the crucial link between gut health and mental well-being, emphasising the need to maintain a healthy gut microbiome for optimal brain function.

Inflammation and Immune Function
Furthermore, the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in modulating inflammation and immune function, both of which are intricately linked with mental health. Dysregulated immune reactions and persistent inflammation have been implicated in the development of mood disorders, underscoring the essential role of gut health in preserving a harmonious immune system.

Practical Tips for Gut Health:
- Eat a diverse range of plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts.
- Incorporate fermented foods like yoghourt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi into your diet to boost probiotic intake.
- Minimise processed foods, sugary snacks, and artificial additives, which can disrupt gut microbial balance.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or mindfulness.
- Prioritise quality sleep by establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a conducive sleep environment.
Conclusion
Understanding the profound link between gut health and mental well-being reveals the intricate interconnectedness of human health. Through adopting dietary and lifestyle changes aimed at supporting our gut microbiome, we can significantly enhance our mental health and overall sense of wellness. Acknowledging and nurturing this symbiotic relationship between the gut and brain provides promising opportunities for fostering mental well-being and averting mental disorders. As we delve deeper into unravelling the complexities of the gut-brain axis, it’s essential to appreciate the significant role gut health plays in our quest for holistic well-being.


